Water-Stable Silver-Based Metal–Organic Frameworks of Quaternized Carboxylates and Their Antimicrobial Activity
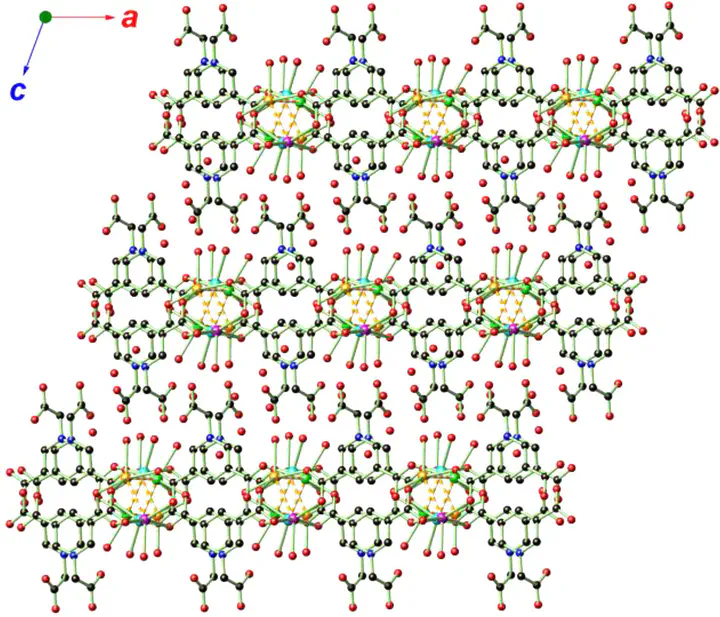 Two-dimensional structure formed from Ag+
Two-dimensional structure formed from Ag+
Abstract
Three-dimensional (3D) and two-dimensional (2D) Ag-based zwitterionic metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) [Ag2(Cedcp)]n (1, 3D, H3CedcpBr denotes N-(carboxyethyl)-(3,5-dicarboxyl)-pyridinium bromide) and {[Ag4(Cmdcp)2(H2O)4]·4H2O}n (2, 2D, H3CmdcpBr denotes N-(carboxymethyl)-(3,5-dicarboxyl)-pyridinium bromide) have been prepared and investigated for antimicrobial activity via minimal inhibition concentration (MIC) test and killing kinetic assay. Both MOFs 1 and 2 show good water stability and solubility ascribed to their characteristic aromatic rings and positively charged pyridinium of the ligands, as well as the presence of Ag+ on their surface, leading to strong antimicrobial activity and a wide antimicrobial spectrum toward Gram-negative and positive bacteria. The results indicated that MOF 2 possesses a faster antibacterial activity (60 min) than MOF 1 (120 min). Scanning electron microscopy analysis further suggests that the Ag-based MOFs are capable of rupturing the bacterial membrane, leading to cell death. Moreover, both MOFs exhibit little hemolytic activity against mouse erythrocytes and show good biocompatibility in vitro, rendering MOFs 1 and 2 potential therapeutic agents for diseases caused by bacteria.